Understanding SWIR Imaging
IR radiation extends from the red edge of the visible spectrum of light across a wavelength range of approximately 500 – 2200 nanometres (nm). Within that spectrum are four distinct wavebands: near-infrared (NIR), SWIR, MWIR, and LWIR. How objects emit or reflect IR radiation is indicative of various physicochemical and thermal properties. For instance, materials exhibit characteristic SWIR absorption / reflection characteristics based on their distinct chemistries, enabling SWIR imaging to detect specific materials remotely.
SWIR refers to the portion of IR radiation adjacent to NIR, occupying a nominal wavelength range of 1,400 – 3,000 nm. We describe these wavelength ranges as approximations as there is no definitive standard of where each waveband separates…
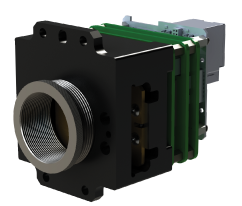
Cooled VGA SWIR InGaAs Camera
Quantitative SWIR imaging and surveillance
The Cooled VGA SWIR InGaAs Camera uses selected InGaAs focal plane arrays with low dark current and low defective pixel count. Thanks to efficient...

Cooled qVGA SWIR InGaAs Camera
Quantitative SWIR imaging and spectroscopy
The Cooled qVGA SWIR InGaAs Camera uses selected InGaAs focal plane arrays Key Features with low dark current and low defective pixel count. Thanks to efficient...